Hours when generation was
mostly non-responsive.
ACER’s hydrogen monitoring report foresees that Europe is likely to miss its 2030 renewable hydrogen targets

ACER’s hydrogen monitoring report foresees that Europe is likely to miss its 2030 renewable hydrogen targets
What is it about?
Europe's Hydrogen and Gas Decarbonisation legislation (2024) tasks ACER with monitoring the emerging hydrogen market.
ACER’s first hydrogen monitoring report highlights that, despite ambitious EU strategies, hydrogen projects face risks from uncertainties of future hydrogen demand and high costs.
What are the main findings?
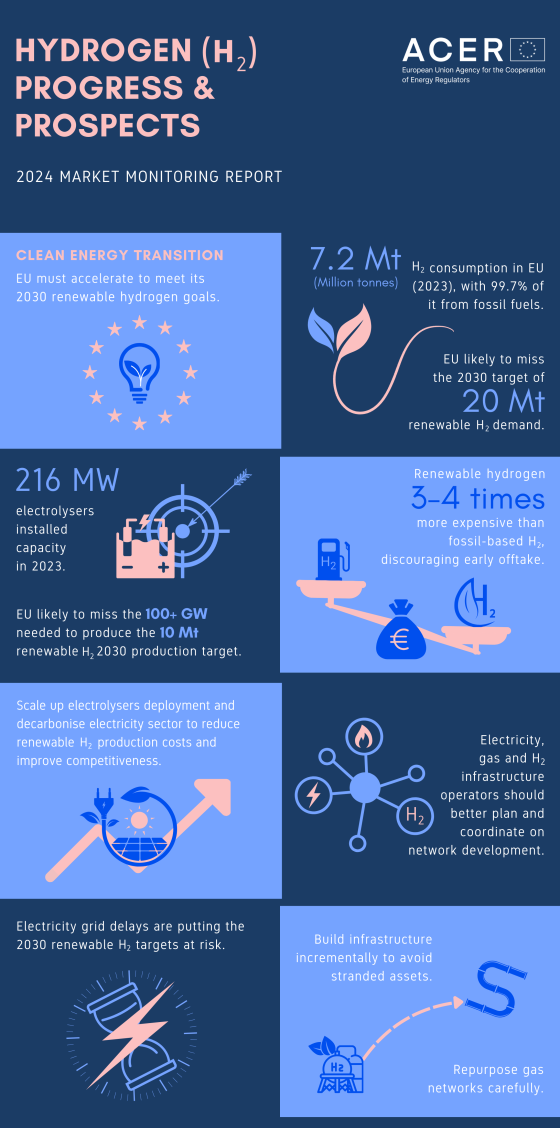
- Low hydrogen demand: The EU is likely to miss the 2030 strategic goal of 20 Mt renewable hydrogen consumption, as current consumption at European level is 7.2 Mt (99.7% of it produced from fossil fuels). EU renewable energy and decarbonisation targets can increase demand for renewable and low-carbon hydrogen by 2030, but so far uptake has been slow.
- Limited electrolyser capacity:
- Total installed capacity of electrolysers in Europe in 2023 was 216 MW.
- Further 70 GW planned for 2030 announced but few are advanced.
- Overall planned capacity is less than the 100+ GW needed to reach EU’s 10 Mt renewable hydrogen production target by 2030.
- High costs prevent renewable hydrogen uptake: The cost of renewable hydrogen is currently 3 to 4 times higher than hydrogen produced from natural gas, discouraging its early offtake.
- Significant infrastructure planned but they face uncertainties in being realised:
- 42,000 km of hydrogen pipelines, numerous storage projects and terminals are planned for the next decade, but only 1% has reached final investment decision, as future hydrogen demand uncertainties pose significant challenges to project promoters.
- Integrated planning by network operators is needed to ensure grid development at sufficient pace and to optimally locate electrolysers.
What are ACER’s key recommendations?
- Quickly transpose the EU (2024) hydrogen and decarbonised gas laws into national legislation and implement them.
- Speed up electrolysers deployment and decarbonisation of electricity sector to increase renewable hydrogen’s cost competitiveness.
- Improve forecasting and accelerate integrated planning to identify realistic hydrogen infrastructure needs, avoiding overinvestments and reducing costs related to under-recovery risks.
- When future demand is highly uncertain, consider incremental infrastructure development based on market needs (to avoid building too much network too fast and stranded assets).
- Consider carefully the repurposing of gas networks for hydrogen to minimise costs, while not overlooking the potential impacts on the broader gas sector (including security of gas supplies).
- Swiftly address demand risk in financing hydrogen networks.
- Provide market certainty over the role of non-renewable, low-carbon hydrogen.
Do not miss the ACER webinar: Europe’s emerging hydrogen market on Tuesday, 3 December (10:00 – 11:00 CET). Register for free and debate with our experts!